Optimal Game of Checkers
Optimal Game of checkers using alpha beta pruning and Message Passing Interface
This project is maintained by AboorvaDevarajan
AI Implementation for the game of Checkers
Objective:
Artificial Intelligence algorithm implementation for predicting the best possible move that can be made by the machine in the game of checkers.
Checkers (English-Draughts)
The game is played on a 64 square checkerboard with eight rows of alternating dark and light colored squares.
There are two players and each player will begin the game with 12 draughts, each player having their own color. The players will place their draughts on the three rows of dark squares which are closest to them. The players will then begin playing, making one move at a time.
The object of the game is to make it so the opponent can’t move when it comes to their turn. This is done by taking all of their pieces throughout the game, or blocking them so they have nowhere to move. The single draughts can only move in a forward diagonal direction into a square without another piece in it. If an opponent’s piece is in the next square, the player can jump it and capture it, removing the piece from the board. They can only do this if the next square is empty. Players can never jump over their own piece.
When a player makes their way all the way across the board to the other player’s side, their piece will be turned into a “King.” When this happens, one of their previously taken pieces will be put on top of the piece which made it to that side.
Once a piece is made into a king, it will be able to move forward and backward, giving it more chances to capture the opponents pieces. A king can jump as many times as it is able to with regards to the necessary squares being unoccupied. However, kings cannot jump over pieces which are the same color as them.
As previously mentioned, the game will come to an end once a player can no longer make a move. If both the players can’t move anywhere, the game will end in a tie, or dblob. Anyone that wants to play on-line will be able to find many different gaming sites which allow them to play. They can play against the computer, or play against other on-line players. There are clubs where players get together in person to compete against each other.
N-ary Game Tree:
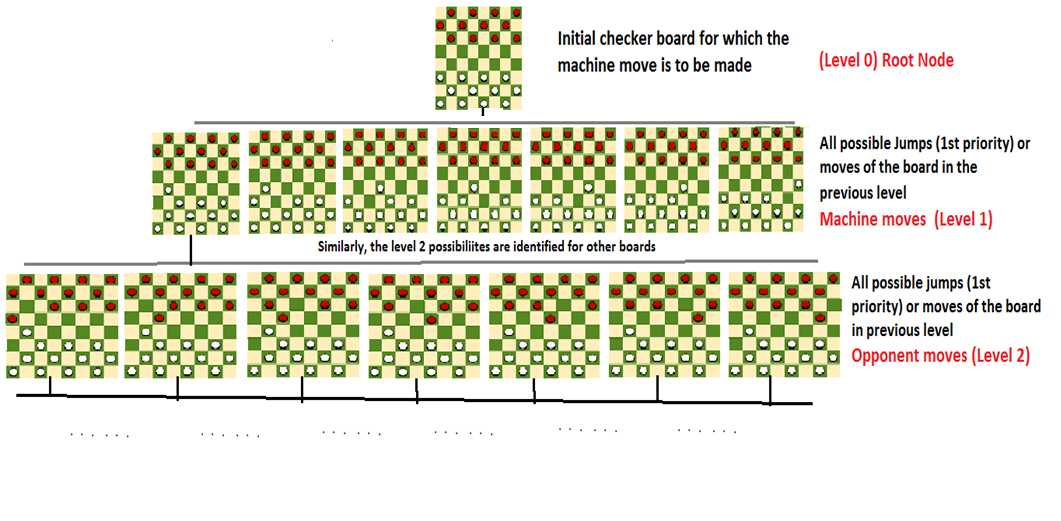
For finding the optimal move of the checker board that can be made by the machine, N-ary Game tree is generated based on the contemporary state of the checker board by fixing the depth. The N-ary Game tree is generated as follows.
Step 1: The initial node that is the root node consists of the contemporary state of the checker board.
Step 2: And the forthcoming levels of the tree consist of all possible moves that can be made by the machine and the opponent alternatively.
Step 3: Step 2 is repeated until the game tree of depth n gets generated.
Step 4: Heuristic value is calculated for all the leaf nodes of the game tree.
Heuristic Value:
For a checker board
- The pawns of the machine are given value 1.
- The Kings of the machine are given value 2 (since these are favorable for the machine to win)
- The pawns of the opponent are given value -1(since these are less favorable for the machine to win)
- The kings of the machine are given value -2 (since these are unfavorable for the machine to win)
And the sum of those values present in the checker board is calculated and it is known as the heuristic value of the checker board, more the heuristic value more the favor for the machine to win the game.
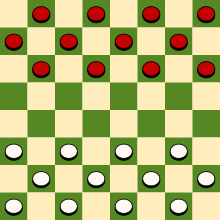
For the above checker board
Number of Opponent pawns = 12 (-1) - -12
Number of Machine pawns = 12 *1 - 12
Number of Opponent kings=0(-2) - 0
Number of Machine kings=0*2 - 0
Heuristic value - 0
Step 5: Mini Max algorithm is used to find the best possible move that can be made by the machine
Optimization of Mini Max: (Alpha Beta Pruning Algorithm)
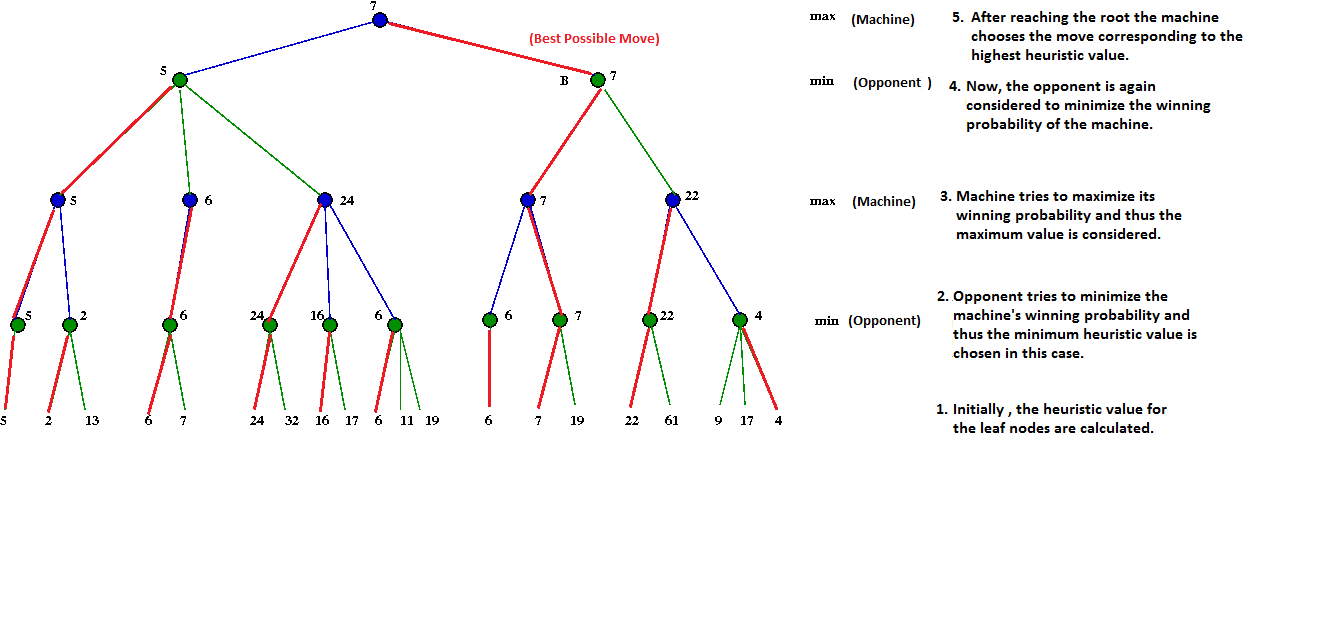
Thus, by increasing the depth of the tree the best optimal move that can be made by the machine can be identified.
Parallelization of Game Tree using MPI (Message Passing Interface):
The winning chances of the machine is increased by increasing the depth of the game tree. In order to increase the time efficiency the algorithm is parallelized using MPI.
MPI that runs on shared memory is used to parallelize since there is a use of pointers to generate game tree.
Parallelization is done for two cases:
1) Game tree generation
2) Game tree traversal.
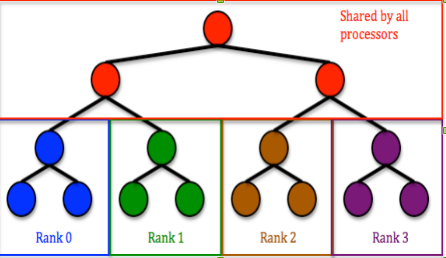
For both the cases the tree is parallelized at the depth=2 considering the depth of the root to be 1.
Hence, all nodes till depth 2 are shared by all processors. The following figure represents the parallelization mechanism.